
Speed Breeding for Crop Improvement
- Home
- Speed Breeding for Crop Improvement

Speed Breeding for Crop Improvement

In conventional plant breeding, after making crosses between desired parents, selection and screening for the desired traits along with generation advancement of the selected material is time consuming and thus 8-10 years are required for development of new variety. This slow improvement rate is attributed partly to the long generation times of crop plants. To increase productivity and stability of crops to meet the changing climatic conditions, there is need to fast-track research and also increase the rate of cultivar development. The time needed for generation of most crops poses a bottleneck in research and breeding programs thereby creating the need for technologies which accelerate plant development process and hence, generation turnover. This major problem can be conveniently overcome by use of speed breeding which involves quickening the breeding cycle from seed to seed by manipulating the photoperiodic conditions along with environmental conditions like soil media composition, temperature, spacing in the glass houses, all done to achieve rapid generation advancement.
Speed breeding in completely controlled and enclosed growth chambers can be used for accelerating plant studies and development, and can also complement in studying mutants and transformation studies.
Using controlled lighting and temperature control conditions plants complete their traditionally long breeding cycle in relatively shorter time by decreasing their time to flower and obtaining seed set, thereby increasing the number of generations obtained per year
Core Recipe of Speed Breeding:
The main ‘recipe’ for setting up speed breeding conditions includes:
1. Light: the preferable light for use in speed breeding is one covering the Photosynthetically Active Radiation(PAR) i.e. 400–700 nm with focus on red, far-red and blue range. This spectrum can be achieved by using Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), or a combination of LEDs and halogen lamps. Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density (PPFD) of ~450–500 μmol/m2 /s at plant canopy height is also recommended which can be adjusted at slightly lower or higher levels according to need of crop.
2. Photoperiodic regime: A photoperiod of 22 hours light and 2 hour darkness in diurnal cycle of 24hoursisideal photoperiodic regime for speed breeding. Another alternative is continuous light but slight period of darkness is known to improve the health of plant.
3. Temperature: Ideal temperature for each crop should be applied. During photoperiod higher temperature should be maintained, while during dark period fall in temperature can help with stress recovery. Temperature has a major impact on the rate of plant development; therefore, generation time can be accelerated bye elevating temperature. However, in some cases higher temperature may induce stress like conditions and affect performance of plant.
4. Humidity: Control over humidity even in controlled environment chambers is limited, but 60–70%RHisideal for crop growth, this level can be modified according to type of crop. For crops more adapted to arid conditions, lower humidity level is recommended.
Innovation Of Speed Breeding:
Speed breeding takes the advantage of an artificial environment with increased duration of light to create the impression of longer daylight period to fasten the breeding cycles of the photo insensitive crops. This results in early reproduction of the crops by making use of continuous light. The speed breeding experiments in wheat have shown that comparison of quality and yield between plants grown under controlled conditions and those grown in regular glasshouse conditions was the same.
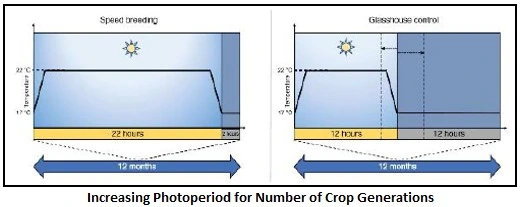
Increasing the photoperiod
Meaning the duration of light exposure each day can indeed accelerate the generations of crops in several ways
- Shortened Reproductive Cycle: Plants typically transition from vegetative growth to reproductive growth based on day length (photoperiod). By increasing the photoperiod, plants perceive longer days and shorter nights, which can trigger earlier flowering and seed production. This shortens the time it takes for each generation to complete its life cycle.
- Continuous Growth: In environments with extended photoperiods, plants can grow continuously without the seasonal cues that trigger dormancy or slower growth phases. This uninterrupted growth allows for faster development through successive generations.
- Year-Round Production: In regions where natural daylight is limited or seasonal, maintaining longer photoperiods in controlled environments (like growth chambers) enables year-round cultivation and breeding. This can dramatically increase the number of generations that can be produced annually compared to traditional field conditions.
- Rapid Genetic Selection: Faster generations mean quicker turnover for genetic selection and breeding experiments. Researchers can observe and select desirable traits across multiple generations within a single year, accelerating the breeding process for developing new crop varieties.
- Climate Adaptation: Speeding up generations through increased photoperiods also helps in adapting crops to changing climate conditions. Researchers can rapidly test and develop crop varieties that are resilient to new environmental challenges such as temperature fluctuations or altered growing seasons.
Increasing the photoperiod in controlled environments like growth chambers or greenhouses can significantly increase the number of crop generations per year. This capability is crucial for advancing agricultural research, breeding programs, and ensuring food security in the face of global challenges.


Speed breeding growth chambers are specialized environments designed to accelerate plant growth and development, primarily used in agricultural research and crop breeding. Here are key details about them:
1. Lighting: Speed breeding chambers use high-intensity, broad-spectrum lighting systems such as LED (Light Emitting Diode) arrays. These provide specific wavelengths of light that promote photosynthesis and regulate plant growth cycles.
2. Temperature and Humidity Control: Chambers maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels to mimic ideal growing conditions for various plant species. Typically, temperatures range from 20-25°C (68-77°F), and humidity is kept between 60-70%.
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Enrichment: CO2 levels are often elevated (around 1000 ppm) to enhance photosynthesis rates and overall growth.
4. Automation and Monitoring: Advanced systems control lighting schedules, temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels automatically. Sensors monitor these parameters closely to ensure stable conditions.
5. Modular Design: Chambers are often modular, allowing researchers to customize growth conditions for different plant species or experimental needs. They can vary in size from small, benchtop units to large walk-in chambers.
6. Benefits: The primary advantage of speed breeding chambers is the accelerated growth and development of plants. This allows researchers to shorten breeding cycles, produce multiple generations of crops in a year, and study plant responses to environmental stresses or genetic modifications more rapidly.
7. Applications: These chambers are used extensively in crop improvement programs, where rapid breeding is crucial to develop new varieties that are resilient to changing environmental conditions, pests, or diseases.
Overall, speed breeding growth chambers play a vital role in modern agriculture and plant science by providing controlled environments that optimize plant growth rates and enable accelerated research and development.
Comment (1)
Leave A Comment Cancel reply
- Blog Categories
- Basic of Artificial Lighting for Plants
- Basic of grow Light
- Case Studies
- General Awareness
- Indoor Vertical Farming
- Medical Plant Research
- Online Tool
- Pitch Grow Light
- Plant Lighting Measurement
- Speed Breeding
- Supplemental Lighting
- Tissue Culture Grow Lights
- Vertical Green Wall
- LED Grow Lights
- Pharma Segment
- General
Popular Products

Enquire Now
Quick Link
Other Links
Design & Developed By VBTEK
































test
demo