
Understanding Difference between PAR vs ePAR
- Home
- Understanding Difference between PAR vs ePAR
Understanding Difference between PAR vs ePAR
In the context of plant light absorption patterns, ePAR and PAR refer to different ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum that are critical for photosynthesis and plant growth.
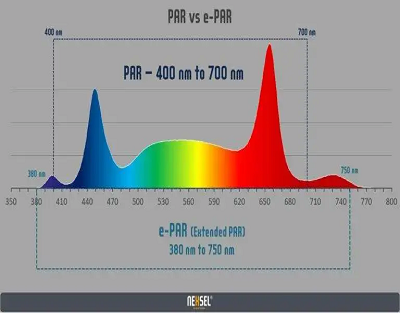
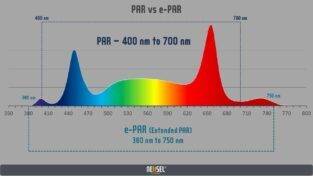
PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation) refers to the range of wavelengths within the visible light spectrum (400-700 nm) that plants can use for photosynthesis. It includes blue, green, and red light, which are efficiently absorbed by chlorophyll pigments in plants.
ePAR (Effective Photosynthetically Active Radiation) is an extended concept that includes wavelengths outside the visible spectrum, such as near-infrared and ultraviolet light. (380-750) Although plants can absorb some of this light, its effectiveness in driving photosynthesis is generally lower compared to the wavelengths within the PAR range.
In summary, PAR represents the range of visible light wavelengths (400-700 nm) crucial for photosynthesis, while ePAR extends this range to include additional wavelengths outside the visible spectrum that can also have some impact on plant growth.
In above article we tried to understand following FAQ’s
What is ePAR?
Difference between PAR and ePAR
Role of PAR light in plant light absorption patterns?
To know more you can reach us on [email protected]
- Blog Categories
- Basic of Artificial Lighting for Plants
- Basic of grow Light
- Case Studies
- General Awareness
- Indoor Vertical Farming
- Medical Plant Research
- Online Tool
- Pitch Grow Light
- Plant Lighting Measurement
- Speed Breeding
- Supplemental Lighting
- Tissue Culture Grow Lights
- Vertical Green Wall
- LED Grow Lights
- Pharma Segment
- General
Popular Products

Enquire Now
Quick Link
Other Links
Design & Developed By VBTEK
































Leave A Comment