
Optimizing Light for Fruiting Plants
- Home
- Optimizing Light for Fruiting Plants

Optimizing Light for Fruiting Plants

Light is one of the most crucial factors in the successful growth and fruiting of plants. Optimizing light conditions can significantly enhance photosynthesis, boost plant health, and increase fruit yield and quality. This article explores various strategies to maximize light efficiency for fruiting plants, whether grown indoors, in greenhouses, or in polyhouses.
1. Understanding Light Requirements
Fruiting plants typically require a higher intensity of light compared to foliage plants. The three main components of light crucial for plant growth are:
• Intensity: The amount of light received by plants, usually measured in lux or foot-candles. Ensure that the light intensity is neither too high, which can cause leaf burn, nor too low, which can result in weak growth. Adjust the distance between the lights and the plants based on their response【13†source】
• Duration: The length of time plants exposed to light each day. Different plants have varying photoperiod requirements. For instance, tomatoes and peppers thrive with around 12-14 hours of light per day, while leafy greens might need up to 16 hours【13†source】.
• Quality: The spectrum or wavelength of light, with blue and red light being the most beneficial for photosynthesis and flowering.
2. Natural Light Optimization
For outdoor or greenhouse-grown plants, optimizing natural light involves:
• Orientation: Positioning plants or greenhouse structures to maximize exposure to sunlight. For example, greenhouses oriented east-west receive more sunlight throughout the day.
• Shading: Using adjustable shading systems to prevent excessive heat and light stress during peak sunlight hours.
3. Artificial Lighting
In indoor growing environments or during seasons with limited natural light, artificial lighting becomes essential. The two most effective types of artificial lights for fruiting plants are:
• LED Grow Lights: LED lights are highly recommended due to their energy efficiency and ability to emit specific light spectrums tailored for different growth stages. They produce less heat compared to traditional lighting, allowing better temperature control【13†source】. Advanced LED systems enable precise control over light intensity and duration, critical for optimizing plant growth fruiting plants【12†source】.
• HID (High-Intensity Discharge) Lights: Including Metal Halide (MH) and High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) lights, HID lamps are powerful and effective but consume more energy and produce more heat than LEDs.
4. Importance of Colour Temperature in Plant Growth
Colour temperature plays a significant role in the growth and development of plants. It refers to the colour of light emitted by a light source and is measured in Kelvin (K). Different colour temperatures have varying effects on plant physiology, including photosynthesis, flowering, and fruiting.
• What is Colour Temperature: Colour temperature is a characteristic of visible light that determines its warmth or coolness. It is measured on the Kelvin scale, with lower temperatures representing warmer, reddish light, and higher temperatures indicating cooler, bluish light.
• How is Colour Temperature Measured: Colour temperature is measured using a Kelvin scale, which ranges from around 1,000K (warm red) to 10,000K (cool blue). The colour temperature of light influences the spectral distribution and intensity of wavelengths emitted, affecting plant growth and morphology.
Impact of Colour
• Temperature on Plants: The colour temperature of light significantly influences various physiological processes in plants, including photosynthesis, photomorphogenesis, and photoperiodism. Different wavelengths of light are absorbed by plant pigments, such as chlorophyll and carotenoids, to drive essential biochemical reactions.
• Effects of Different Colour Temperatures on Plant Growth: Warm White (2,700K — 3,500K): Promotes flowering and fruiting, ideal for the flowering stage of plants Cool White (5,000K — 6,500K): Enhances vegetative growth and leaf development, suitable for the vegetative stage Daylight/Full Spectrum (6,500K — 10,000K): Provides a balanced spectrum of light for overall plant growth, suitable for all growth stages【12†source】.
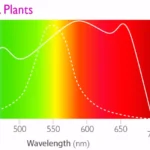
5. Understanding Light Spectrum
Different color of light have varying effects on plant growth:
• Blue Light: Crucial during the vegetative stage, blue light (400-500 nm) promotes strong root development and compact, sturdy growth. It encourages larger leaf surface areas, enhancing the plant’s ability to photosynthesize【12†source】.
• Red Light: Essential for flowering and fruiting, red light (620-750 nm) triggers blooming and increases fruit production. It plays a significant role in the flowering process, leading to higher yields【12†source】.
• Green Light: While often underestimated, green light penetrates deeper into the plant canopy, aiding in uniform growth and facilitating better health inspections without disrupting the plant’s perception of day and night【10†source】.
• UV Light: Small doses of UV light can enhance plant compounds, improving flavor, aroma, and nutritional content. It also helps in stress response and pest resistance【10†source】.
• Infrared Light: Infrared (IR) light influences flowering and stem elongation. While primarily experienced as heat, it’s essential to balance IR exposure to avoid overheating and ensure robust flowering【10†source】.
Tips for Using Artificial Lights
• Positioning: Place lights at an appropriate distance to avoid light burn but ensure adequate coverage. Typically, LED lights should be 12-24 inches above the plant canopy.
• Duration: Fruiting plants usually require 12-16 hours of light per day. Use timers to maintain consistent light schedules.
• Light Cycles: Some fruiting plants benefit from specific light cycles, such as 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness to induce flowering.
6. Reflective Surfaces
Using reflective materials can enhance light distribution and intensity. Reflective surfaces such as Mylar, white plastic, or reflective paint can bounce light back onto plants, reducing shadows and ensuring uniform light coverage.
7. Light Measurement and Monitoring
Regularly measuring light levels ensures that plants receive optimal light conditions. Tools such as light meters can help monitor the intensity and adjust lighting setups accordingly. Additionally, observing plant responses, such as leaf color and growth patterns, can provide insights into the adequacy of light.
8. Seasonal Adjustments
Adjusting light strategies based on seasonal changes is crucial. In winter, supplementing with artificial lights can compensate for shorter days, while in summer, shading might be necessary to protect plants from excessive heat and light.
9. Plant Spacing and Pruning
Proper plant spacing and regular pruning can optimize light penetration and airflow, reducing the risk of disease and ensuring all parts of the plant receive adequate light. Avoid overcrowding, which can lead to shaded lower branches and reduced fruit production.
10. Practical Tips for Optimization
• Start Slow: Introduce new light spectrums gradually to allow plants to adapt.
• Monitor and Adjust: Regularly check plant responses and adjust light settings accordingly.
• Use Timers: Automate light cycles to simulate natural daylight changes, which is especially beneficial for maintaining consistent growth conditions【13†source】.
• Combine Light Sources: Where possible, blend natural sunlight with artificial lighting for the most effective results【11†source】.
Conclusion
Optimizing light for fruiting plants involves a combination of utilizing natural sunlight, implementing effective artificial lighting systems, and employing techniques to ensure uniform light distribution. By understanding and catering to the specific light needs of fruiting plants, growers can enhance photosynthesis, improve plant health, and maximize fruit yield and quality. Whether in an indoor setup, greenhouse, or polyhouse, strategic light management is key to successful fruit production.
- Blog Categories
- Basic of Artificial Lighting for Plants
- Basic of grow Light
- Case Studies
- General Awareness
- Indoor Vertical Farming
- Medical Plant Research
- Online Tool
- Pitch Grow Light
- Plant Lighting Measurement
- Speed Breeding
- Supplemental Lighting
- Tissue Culture Grow Lights
- Vertical Green Wall
- LED Grow Lights
- Pharma Segment
- General
Quick Link
Design & Developed By VBTEK









Leave A Comment